On top of that, I believe that the US government is insolvent. In fact, everybody knows the US is broke but people will stand by and let it happen.
An analogy for the Federal government is the city of Detroit. Five years ago, they already knew that they were broke. But it is not until they finally had to write a check that they could not write that they declared bankruptcy.
Even though the bankruptcy was inevitable, it shocked people. The City of Detroit recently announced that pensioners would get 16 cents on the dollar. Had Detroit faced its budget problems five years earlier, pensioners may have gotten 60 cents on the dollar. Allowing the situation to get worse led to great disappointment and damage.
The Federal government looks about as bad as Detroit five years ago. In financial year 2013 it brought in $2.8 trillion in revenues and spent 3.5 trillion, as reported by the Treasury department. Their current liabilities are something like 87 trillion with a national debt of 17 trillion. The situation is hopeless.
It is propped up by the Fed. When the Fed does an open-market operation, the stocks go up. When they are not doing any such operations, overall, they go down.
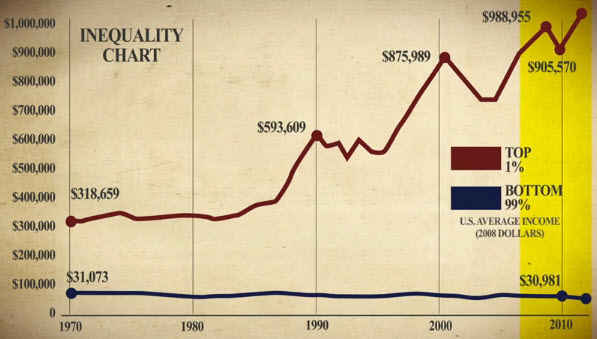
- Source, Eric Sprott:
http://sprottgroup.com/thoughts/